How to Turn a Drawing Into Digital Art With Corel Painter 2015
A COMPLETE SURVEY
Covers the major aspects of digital painting, written for artists, art students, art historians, galleries, curators, collectors and fine art lovers. For a cursory overview run across: DIGITAL PAINTING, a cursory overview
Updated since 2013. Last update April 19, 2022
The data you find here draws on the experience of a handful of pioneering digital painters. It is the oldest and most consummate source of data on the subject. Information technology is independent, revenue-costless and regularly updated. The text has been dedicated into the Public Domain by a CC0 1.0 universal license. You are gratuitous to re-create, print and use it in accordance with the license. The images are protected past copyright unless otherwise stated.
This website attracts thousands of visitors worldwide every month. Digital artists, let collectors know what you are doing while increasing traffic to your portfolio by linking (parts of) this site to yours. Share our endeavour to promote a meliorate understanding of digital painting.
Definition
Visual characteristics
Differences in method, spontaneity, artistic influence
Primary and secondary carrier
Prints and screen representation only
Mainstream directions: calculator generated, raster, vector, mixed media
New photography
Size, resolution, enlargement
Vector and raster painting enlargement
Color
Texture
Painterly development
Collecting digital art, cess
Marketplace for digital art, prints
Quality-quantity convention, limited impress editions
Certification of a print
Market place for digital art, digital file as NFT
Protecting prints and files, NFTs, timestamp
Green NFT art platforms
Disadvantages and risks of NFTs
How to choose NFT platform
Links
Gallery of characteristics
Gallery of computer-generated paintings
Gallery of raster paintings
Gallery of vector paintings
Gallery of vector-raster paintings
Gallery of photograph-based paintings
Gallery of preset styles and conversions
Definition
Definition
A 'digital' painting is created on the estimator using a graphics programme, a virtual paintbox with brushes, colors and other supplies. The definition applies to a painting on its primary digital carrier (as a computer file) every bit well as when information technology is transferred in a non-manual procedure to a secondary physical carrier (printed on paper, acrylic glass, aluminum, sail, etc).
Visual characteristics
Visual characteristics
Apart from the traditional tools, the virtual painting box contains instruments that do not be outside the computer. The use of these instruments distinguish a digital from a non-digital painting. Typical characteristics tin be traced back to the power of the reckoner to attach geometrical formulas to lines and shapes. While it is impossible for a human hand to create exactly identical forms, or to construct a perfect circle or a perfectly direct line, for a computer it is difficult to do anything but this. Vector painting is exclusively based on this feature. Hybrid vector-raster painting and new photography make some use of it. Raster paining past definition uses no formula-based shapes. Yet, digital traits are sometimes present in software-specific brush tips as well as in the mutual flatness of the physical representation. Formula-based shapes are like shooting fish in a barrel to recognize by a degree of perfection that is literally inhuman. They bear some resemblance to newspaper cut-outs or stencil fine art.
Specific digital traits include:
- Sharp transition betwixt colour panes
- Transparency
- Symmetry
- Exact repetition
- Perfect circles, squares and other shapes
- Embossing, shading and other 3D illusion
- Perfectly smoothen gradients
- 100% monochrome color planes
- Absenteeism of brushstroke
- Slalom or flip forms
- Effects of automatic transformations (mirror, ripple, swirl, shear, multiply etc.)
The flatness of the concrete representation is typical for the digital medium. It is possible to create a convincing illusion of texture on the virtual canvas, just not to translate this to existent texture on paper, dibond, perspex etc.
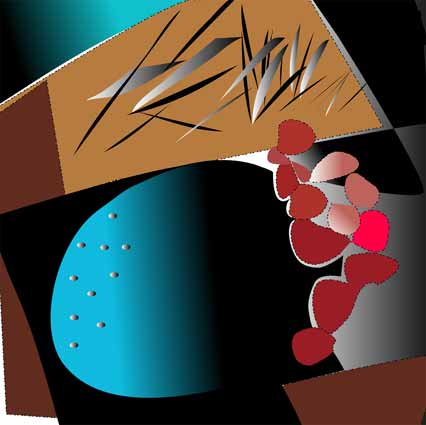

Van de Ven: Wishful Weightwatcher (2015)
-
Gallery of visual characteristics
Definition
Differences in method
Spontaneity
In most programs information technology is possible to undo all or a big number of castor strokes and other actions without a trace. A painting is no longer spoiled by a unmarried brushstroke. The 'undo' choice and many push-button transformations requite digital painters the freedom to work faster, to freely make mistakes and to have a more than experimental and spontaneous arroyo to their work. The creation of estimator 'generated' images in detail is fast, intuitive and spontaneous. It should be noted that vector painting involves the manipulation of shapes with a specific tool, which is a slower and more deliberate process than stroke-past-stroke painting. However, once they are formed, shapes obey one-click operations like alter color, resize, emboss, mirror, group, bandage shadow, etc. which allow for an unprecedented speed and spontaneity.
Artistic influence - A process of creation
While 'art' is usually defined as 'human being' artistic skill and imagination, it becomes increasingly difficult to assess to what extent a painting is the result of human attempt. The influence that the artist exerts on the final result can be assessed by the software, the painting medium that has been used in the procedure and the preferences of the creative person. In traditional painting this influence is past nature 100 percent. This is all the same true for digital raster and vector painting. For figurer-generated the influence is dictated by the software and may vary from 0 to 100 percent. For new photography , the artistic procedure is oftentimes a series of more or less complex automatic transformations that are chosen at vision. In addition, photo's may be used as first layer and worked over with a painting medium. The influence of the creative person is difficult to assess and may vary from 0 to 100 percent.
The post-obit categorization may be useful. Digital painting is:
- A process of structure when the artist originates the paradigm and uses input parameters or a set of rules to determine the concluding result. -A process of play
- A process of selection when the creative person makes a serial of automated push-button transformations and chooses a generated image without changing information technology.
Digital and physical carrier
Primary and secondary carrier
The chief carrier of a digital painting is a computer file.
The secondary carrier is a physical representation of this file afterwards it is transferred to paper, wood, acrylic glass, etc. in an automated procedure - in other words, a impress .
Prints and screen representation just
Prints and screen representation only
Obviously, forms and shapes that are typical for digital painting cannot be transmitted to a physical carrier in a manual process. The digital characteristics would be lost. The implication is often under-emphasized: a digital artwork, in its physical representation, is and can only be a print or an image on a screen. If an artwork that was created on a computer is printed on canvas and painted over with existent paint or a brushstroke gel, the result is a traditional, non digital painting. The original piece of work on the figurer still meets the definition of a digital painting.

Leo Geurts and Lambert Meertens Cristalstructuren (1970)
Mainstream directions: computer generated, raster, vector, mixed media
Mainstream directions
Based on differences in method and appearance, five mainstream directions can exist recognized:
i. Computer-generated painting
2. Raster painting
iii. Vector painting
iv. Hybrid painting and vector-raster combined
5. New photography
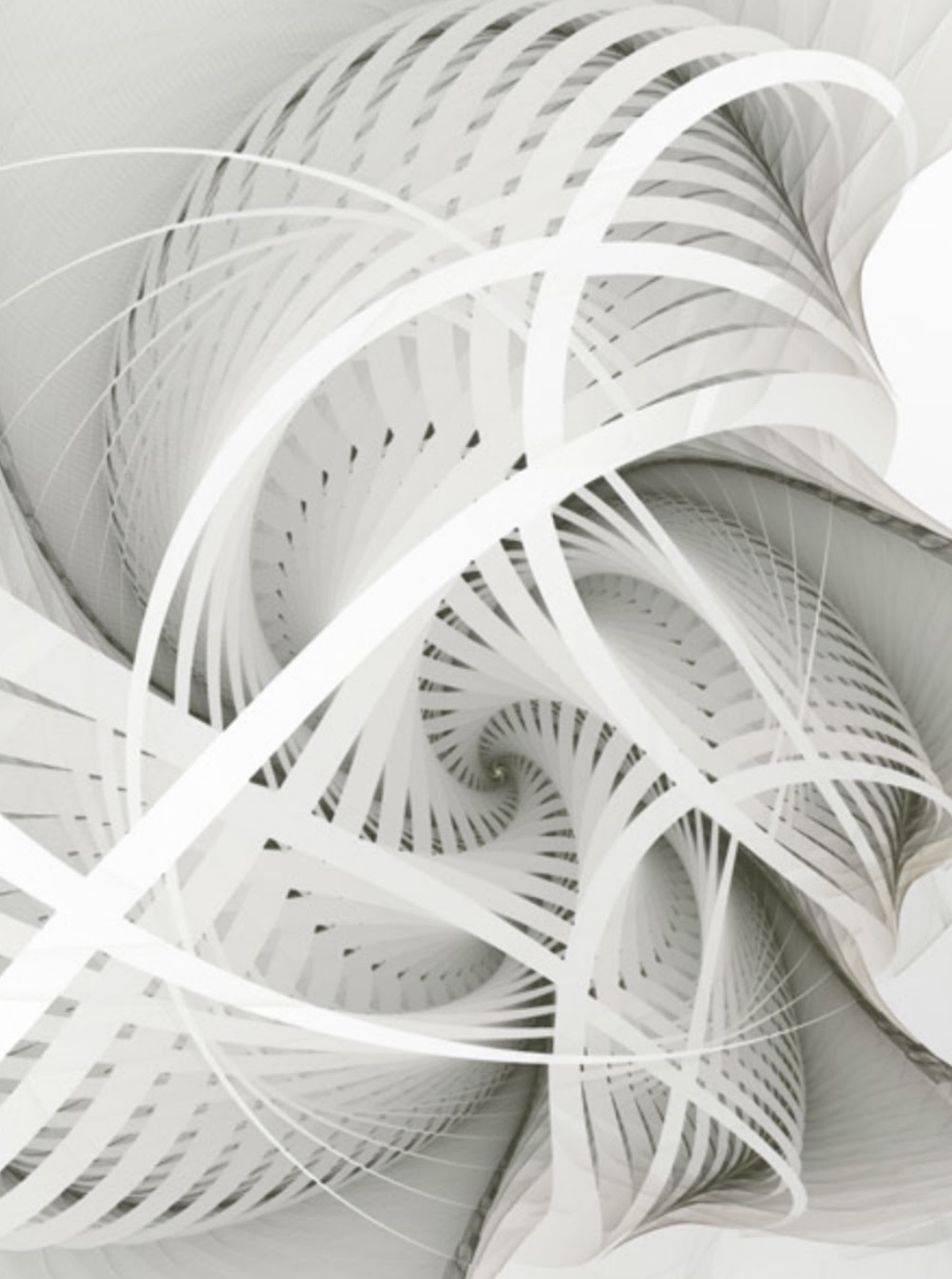

Karin Kuhlmann: In Between 11 (2008)
- Reckoner generated painting
'Computer-generated' does not necessarily hateful that the computer creates the image. The somewhat confusing term 'generated' but refers to the 'easily-off' painting method: the artist doesn't create the artwork by hand, simply instructs the computer how to exercise it. Like a composer who creates music, not past playing it on an instrument but by writing music notes on a score. The method goes back to the early days of artificial intelligence, when Prescriptions for all forms and lines had to be manually described by a mathematical formula. Since the 1970s, the formulas and calculations needed to construct the image are taken care of 'behind the screen'. The influence that the artist exerts on the concluding event varies from 0 to 100 percentage.Fractals
The essence of 'generated' art is the possibility to instruct the computer, in a language of formulas, to create lines, forms and colors. Some of these formulas generate patterns that infinitely repeat themselves. All the same far you zoom in, you will always come across new fragments of the same pattern. These self-repetitive forms are chosen fractals: geometrical shapes that can exist split into parts, each of which is a reduced-size copy of the whole.Mandelbrot gear up (in black). Click the image to zoom in. Mandelbrot set
An infinitely self-repetitive pattern was first studied around 1918 by the French mathematicians Pierre Fatou and Gaston Julia. Their pioneering piece of work was forgotten until Benoit Mandelbrot mentioned them lx years afterward in his work about fractal geometry. In honour of Mandelbrot'south work, others named the specific points generated by Mandelbrots equation (that was similar to that of Fatou and Julia) the 'Mandelbrot set'. In 1978 the American mathematician Robert Brooks first programmed a visualization and thereby introduced fractals in the field of arts.
In painting software, the process to generate Mandelbrot images is predetermined, based on the Mandebrot equation. Personal choices are possible for colors but not for forms. Images are truly generated, the effect of a process of pick.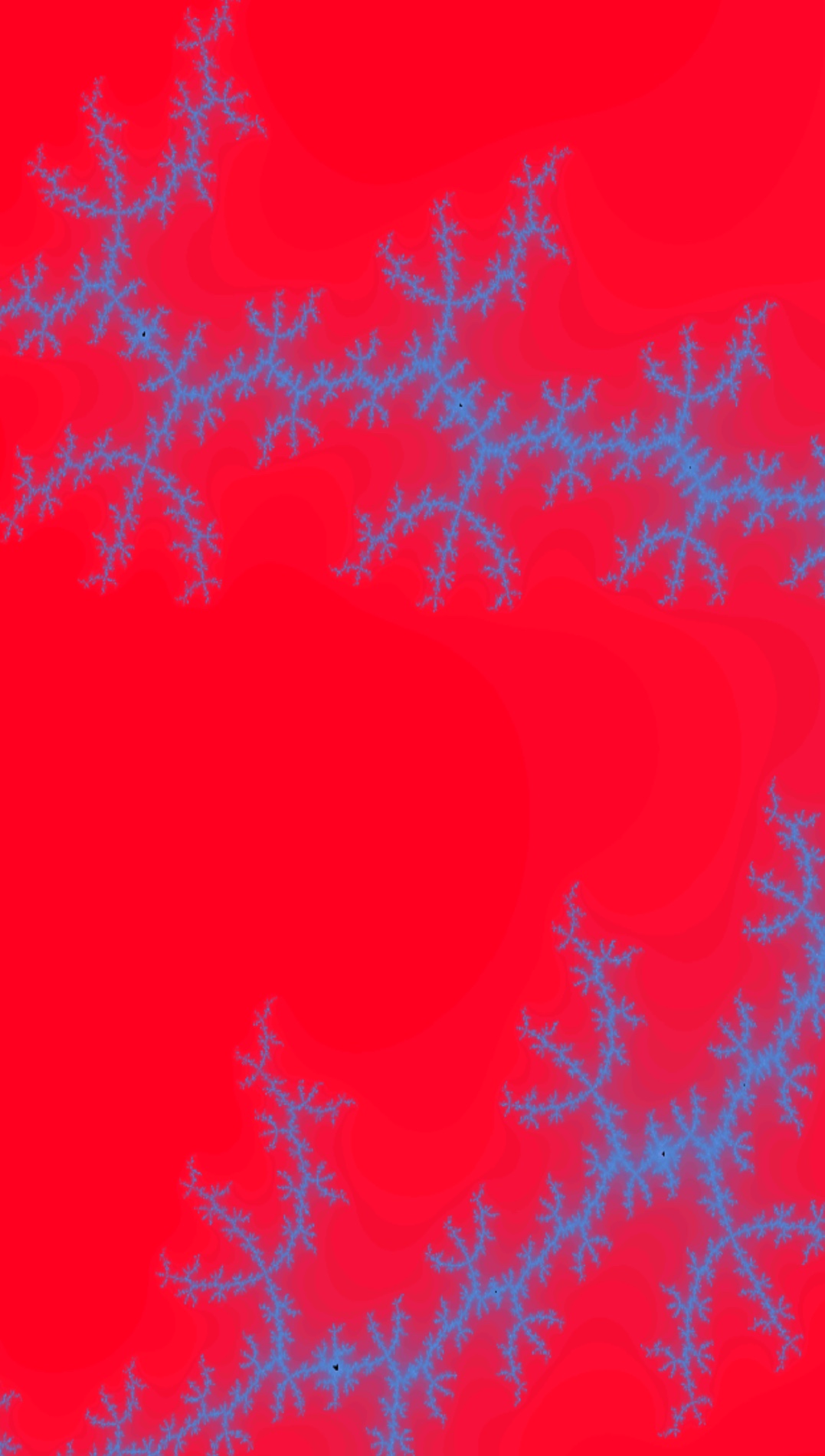
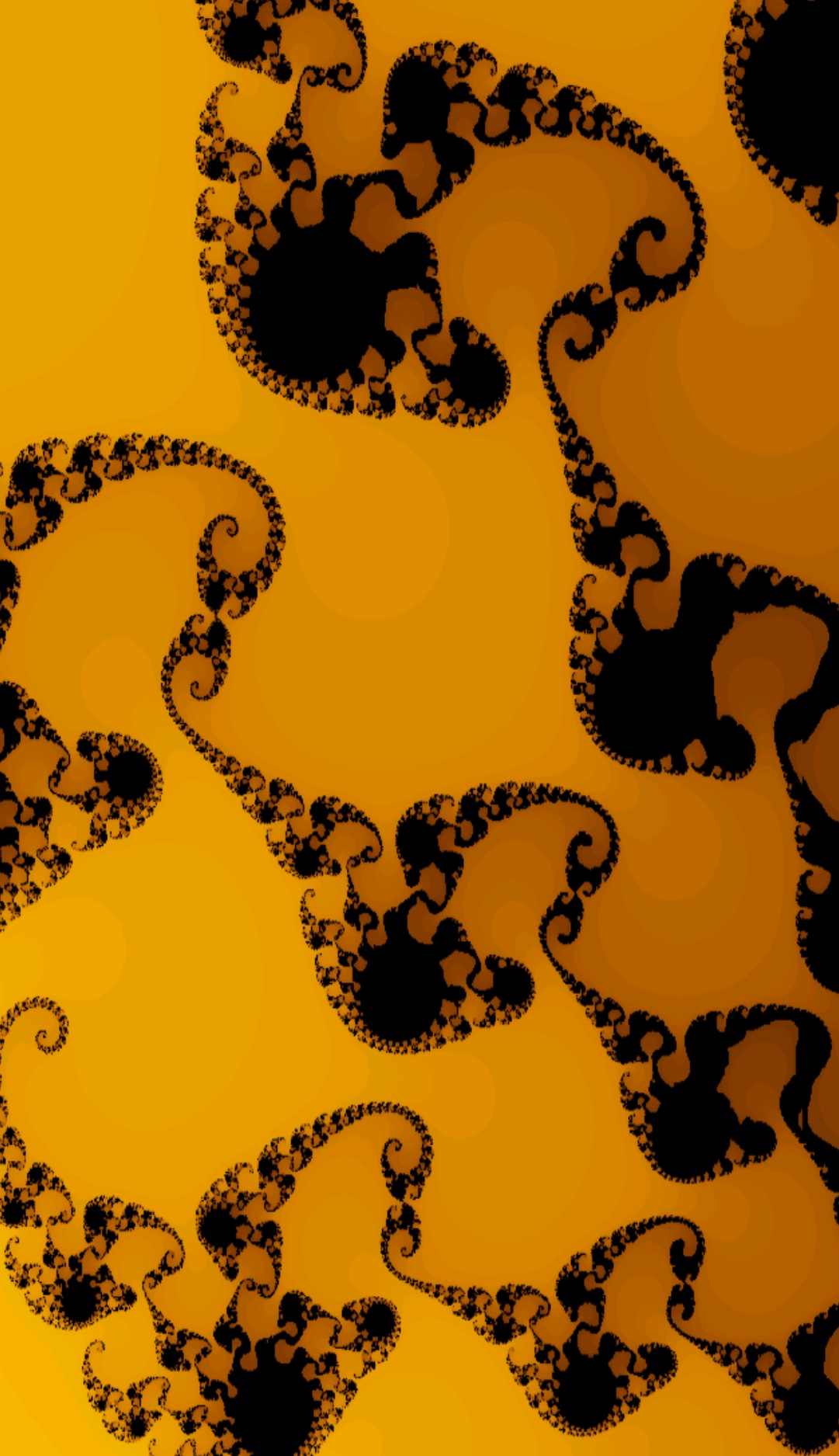


Images created in a procedure of selection by
zooming into the Mandelbrot set (screenshots)
L-systems
In 1968, the Hungarian theoretical biologist Aristid Lindenmayer adult geometrical patterns aimed at describing the growth process of plants. In painting software, this mathematical framework is used to create patterns of lines, shapes and colour. L-systems can as well be used to generate self-similar fractals similar the Mandelbrot gear up. The method is computer-executed, a process of construction. The creative person is able to originate the image, adapt the rules and determine the final result.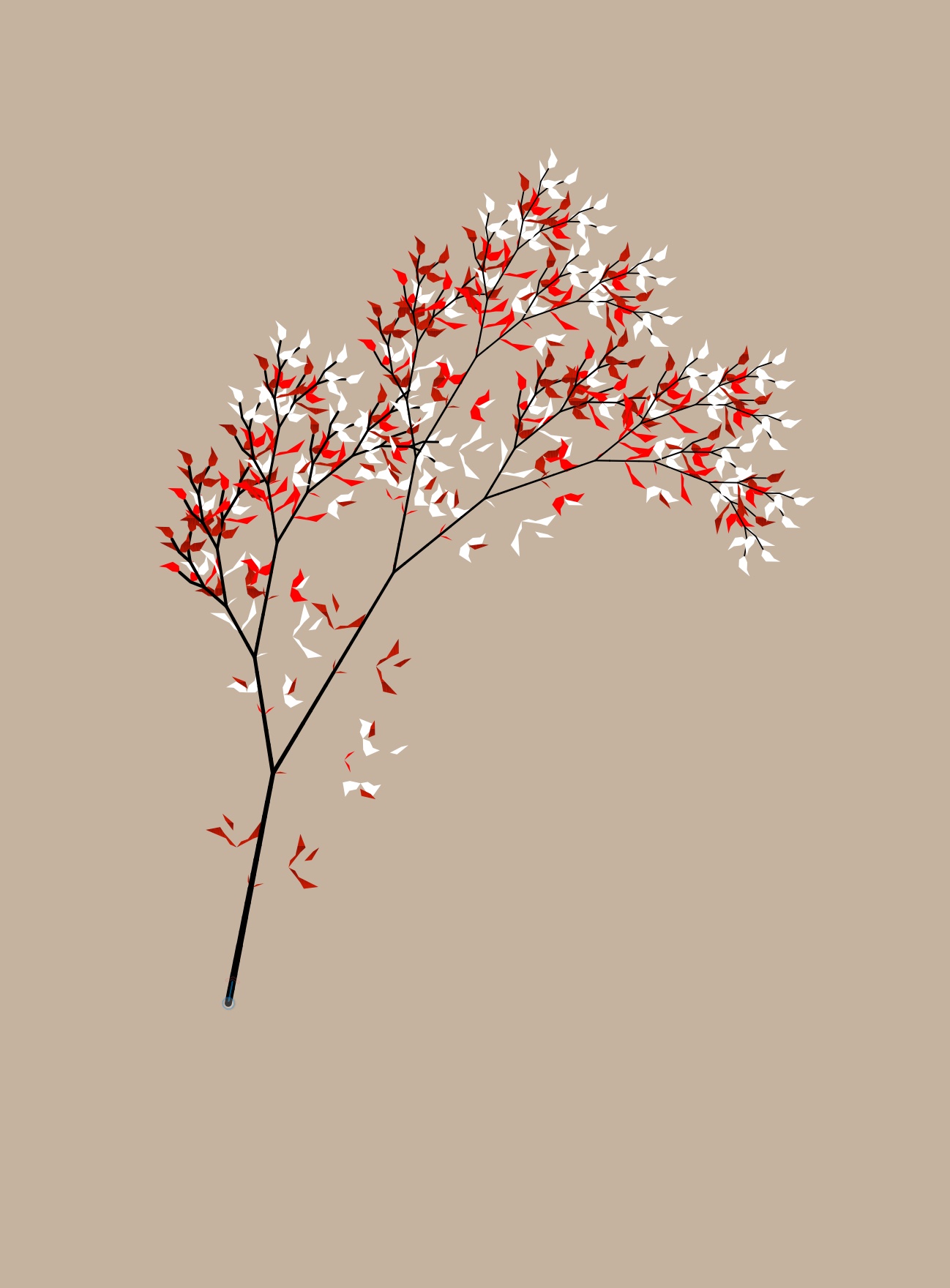
Images created with L-systems software in a process of construction:
'Paper tree' (50.) 'Migration' (r.) (2019)
Stochastic rules
Uncertainty and take a chance are used to generate variations on a theme. The artist makes an initial choice from a gallery of images and uses it to walk a choice path of push-button random transformations for lines, shapes, colors and other parameters. Finally, several parameters can be changed to manually adjust and personalize the image. The method varies from a process of selection to a process of play or a process of structure.
Paradigm created with stochastic rules software in a process of play:

-
Raster painting
In raster painting, colors and lines are registered pixel by pixel on the canvas. In procedure as well as advent, raster, 'grid' or 'bitmap' painting resembles almost closely a traditional painting with real brushes and paint. The image is created on the screen in a stroke-by-stroke way. All the characteristics of the individual painter's mitt are preserved. The only digital trait is the flatness of the physical carrier.Bug with enlargement are the main disadvantage. Often, the length and width of the creation is every bit minor equally a (mobile) calculator screen and the resolution as low as 72 dots per inch. If the epitome is to be transferred to a physical carrier of a customary size that tin hang on the wall, it has to be enlarged considerably. This by and large entails manual correction, a tedious and time consuming process. Transmission enlargement is a serious obstacle for press and selling raster paintings.
In recent versions of some raster painting programs, 'scripting' allows the painter to replay the brushstrokes on a larger sheet on the desktop (run into 'size, resolution, enlargement')Raster paintings are ordinarily stored as a BMP, JPEG, PNG, GIF or TIFF file.
-
Gallery of raster paintings
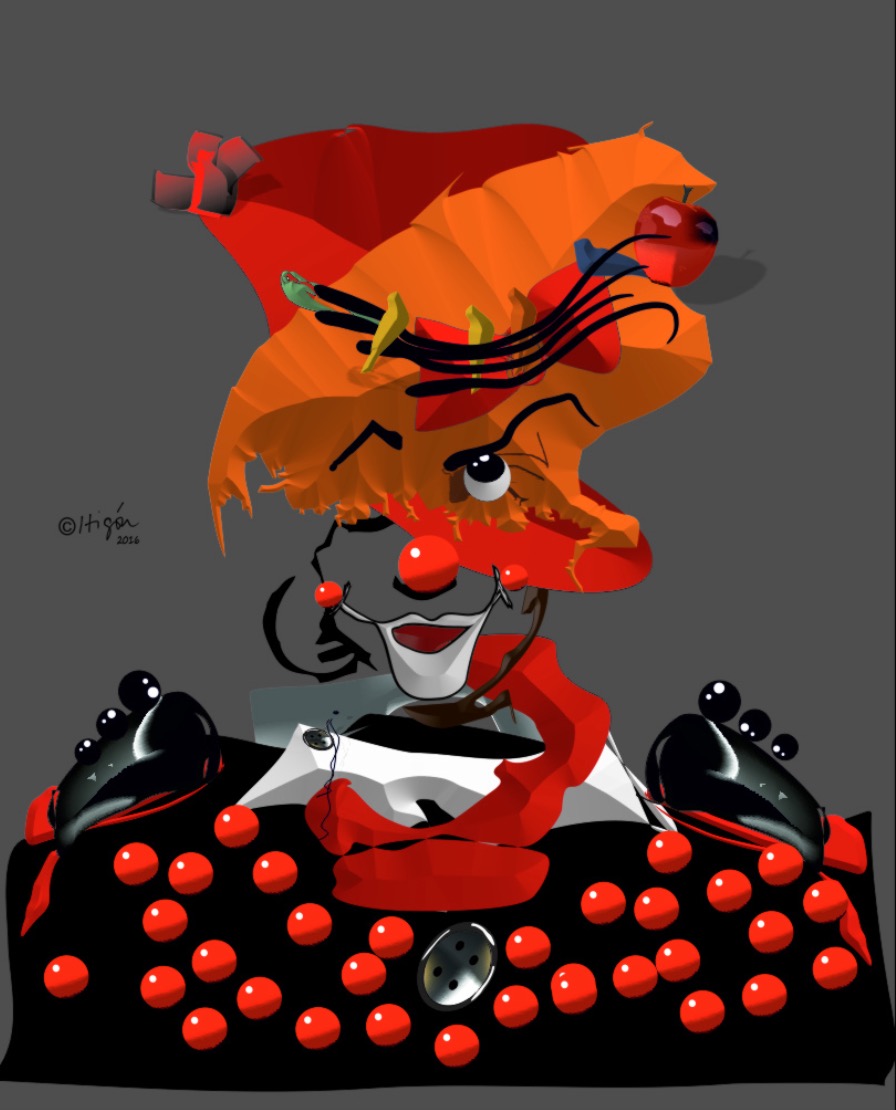

Amparo Higón: Cocky portrait (2016)
-
Vector painting
Together with hybrid- generated-painting and new photography, vector is one of four directions that together create the new visual language that has emerged since painters employ a estimator.
What distinguishes vector from all other forms of digital painting is that it uses the ability of the figurer to capture forms and lines in mathematical formulas. A French engineer, Pierre Bézier, was the first to use the existing mathematical framework to make visual representations. With shine 'Bézier curves' he designed new motorcar models at Renault around 1960. Since so, vector programs have become pop in the world of design and advertising. Digital painters are beginning to explore the medium.The translation of shapes and lines into formulas offers possibilities that cannot exist achieved in any other way. Vector images are size independent; they can be enlarged without loss of resolution. Although the primary process is not very spontaneous - pushing and pulling with a special instrument is reminiscent of sculpture - once they are formed, shapes obey ane-click operations similar modify colour, resize, emboss, mirror, group, cast shadow, etc. This allows for an unprecedentedly swift and intuitive method.
Vector paintings can be recognized by a certain minimalism and a sharp definition of forms that is reminiscent of screen prints and monochrome collages such as those past Matisse. Colors are strictly monochrome or perfect gradients of two colors. In the absenteeism of a brush stroke, other aspects that convey something of the maker's mood or personality such as atmosphere, palette, concept, choice of subject field and composition come up to the fore. Since this is not the case with all digital art, it should be noted that the creative person has complete control over the artistic process.
Vector paintings are commonly stored equally an EPS, PDF, WMF, SVG, or VML file.

-
Mixed media and hybrid painting
Painting media are sometimes combined, either past using different software for the aforementioned painting or by using a program for hybrid painting. Vector-raster painting combines the personal brush style of raster with the formula-based lines and forms of vector. The use of dissimilar software offers maximum contrast betwixt sharp and soft and between the uni- and duo-colors of vector and the broad palette of raster. Other popular combinations are manual vector with figurer generated, and photography with raster or vector painting and with computer 'generated'.
Some hybrid painting programs (e.g. ArtRage) use Bézier curves in the background to smooth lines and curves of raster paintings without intervention of the artist. The painting process is spontaneous, stroke by stroke, and the storage format is raster. The smooth, not-raster, non-vector appearance reflects the hybrid basis. Smoothing mitigates the loss of resolution and eases the job of enlargement when the software does non offer scripting.
Hélène Goldberg: Sunny angle
-
Gallery of vector-raster paintings
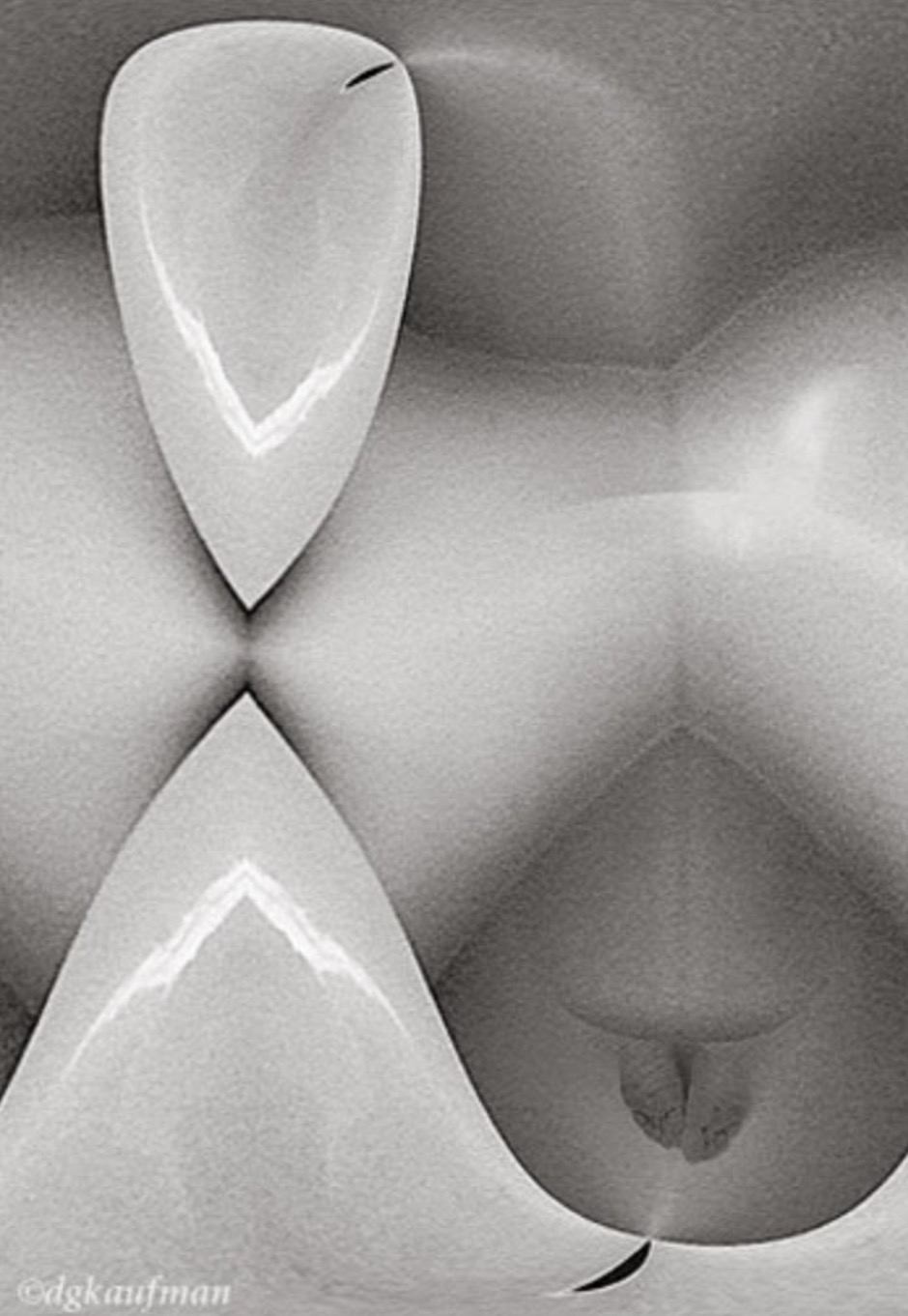

Dolores Kaufman, Inner sanctum (undated)
New photography
New photography
The relation between painting and photography is centuries quondam, but never earlier has it been so close. To place a pic on a digital sheet and transform it into a painting now requires cypher just a push on a button, and a lensman today uses the same software for editing and transforming a photo as the artist for creating a painting. The shared toolbox entails changes in painterly development (below) and creates a new transition zone between painting and photography.
Filters
A diverseness of media filters can make photos or screenshots resemble an oil painting, watercolor, woods-cutting, etching, etc. Manner filters can put them in the visual framework of Seurat, Van Gogh, Pollock and many others, while form filters create effects similar circle, wave, multiply, mirror, swirl and shear, or they tin suspension up the image in a kaleidoscope of geometric forms that radiate from a central bespeak in perfect symmetry.
Mixed media
While these transformations are push-button, they are often office of a more complex method that combines several kinds of photographic, computer-generated and painterly aspects in subsequent stages. A possible workflow might be: a screenshot or photo is taken, subjected to a transformation similar a swirl and put on the canvass as component of a painting. Applied as mixed media, new photography makes an important contribution to gimmicky visual language.
Photograph-based paintings are stored every bit raster files like BMP, JPEG, PNG, GIF or TIFF.

-
Gallery of photograph-based digital art
File formats
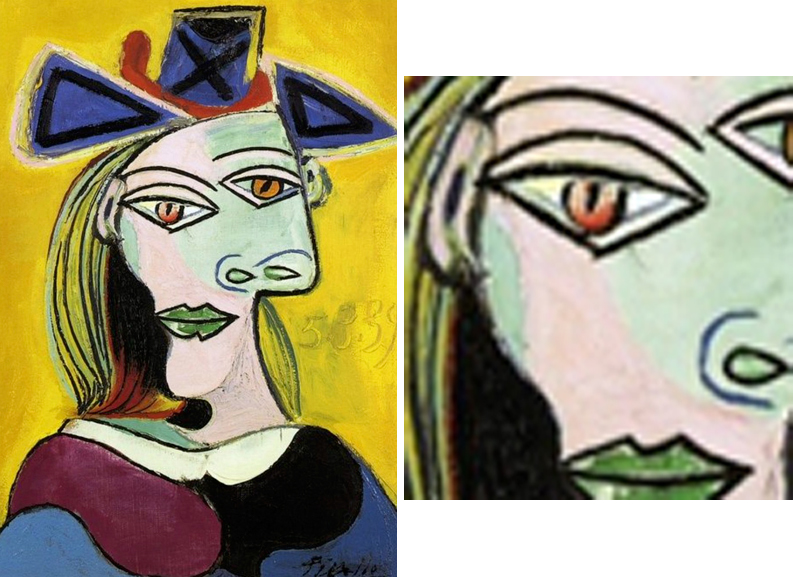

(Enlarge to see the consequence of a 300 pct. resize of a raster image)
Size, resolution, enlargement
Size, resolution, enlargement
When the artist increases the height and width of an existing image, its resolution or information density decreases and it will become vague. Resolution is usually expressed in dpi (dots per inch). While the image on the screen already looks abrupt at the standard resolution of 72 dpi on the spider web, a physical carrier needs 300 dpi or more to wait sharp. Moreover, the physical carrier is usually much larger in height and width equally well.

of the bath (1930) (zoom in)
Correction of raster painting enlargement
Vector and raster painting enlargement
For a vector painting, where colors and lines are controlled by formulas, enlargement requires nothing just a push on a push. There is no loss of resolution. For raster painting, data will accept to be added to fill in the gaps. This is done with the assist of enlargement software or by the 're-size' option in the painting program. Automatic enlargement usually needs transmission corrections.
Although much progress has been made in automatic enlargement, information technology remains difficult to fill in the empty infinite betwixt handmade lines and shapes. Lines get unsteady and crumbly and unintended 'noise' appears forth the edges of colour patches. The image in a higher place shows two different types of online enlargement of the same fragment of Pierre Bonnard's Getting out of the bath. Note that each entails its own noise and deformation.
In order to eliminate deformation and obtain a faithful representation of the original, automatic enlargement is usually followed past transmission correction. Depending on the speed of the computer and the chosen size and resolution of the prototype, correction can be irksome or even come to a halt. The screen, of course, is non enlarged: the artist can no longer see the whole paradigm and has to zoom in and out, switching between corrections and reviewing the results. Depending on the size of the file, the ho-hum and detailed process compares to fine needlework.
Recently, several programs for raster and hybrid painting introduced 'scripting'. Strokes and actions that compose the image are recorded and can exist repeated in an automated process and without loss of resolution on a larger canvass on the desktop.
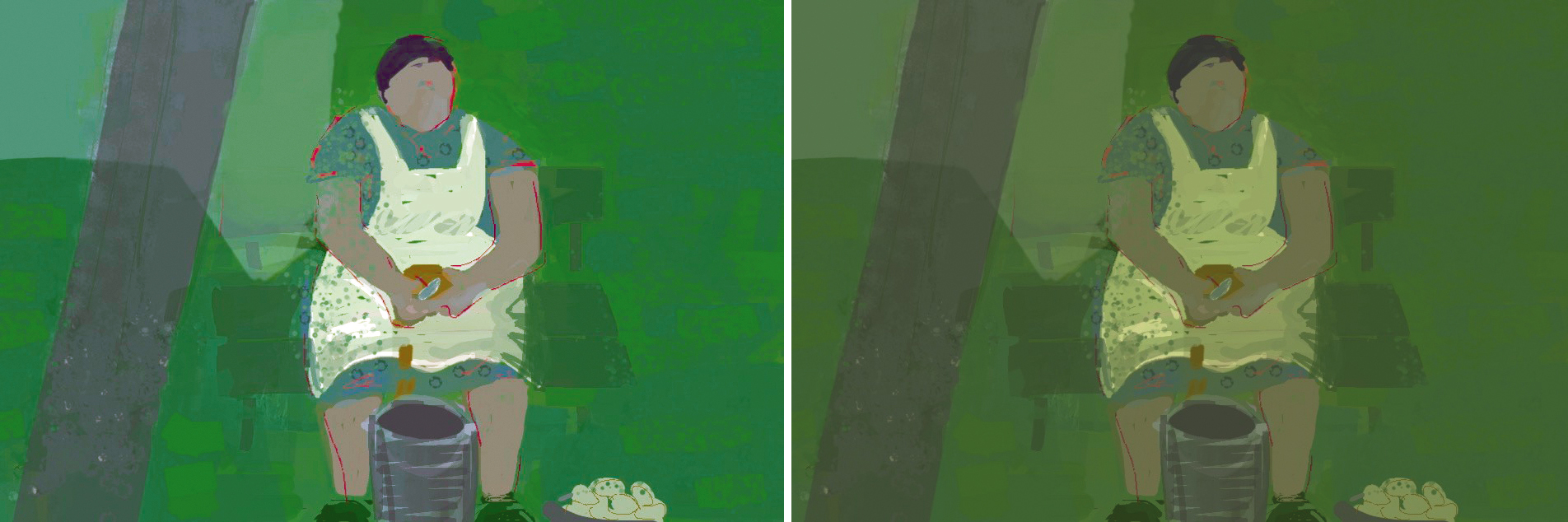

embedded (50). Green cast with an RGB contour for online display (r)
Color
Color
For artists and collectors alike, a true-blue representation of colors is of prime importance.
To see colors
Every figurer screen deviates to some degree from the 'true' colors that are set up as a standard by the international color convention (ICC). These deviations tin can be corrected by a calibration of the screen. For anyone working with colors it is necessary to calibrate the screen regularly. It is done with a pocket-sized sensor that calls up a number of colors on the screen, compares them with the standard values and creates a monitor contour which is automatically installed as the default. It runs silently in the background and has only ane task: to proceed the individual screen fixed to the standard. Although, confusingly, this profile is listed between a whole range of optional profiles for press, it should be left alone. It is non embedded in an artwork.
To create colors
In desktop painting software, the basic profile types have their corresponding palettes and matching color spectrum in the workspace. It is advisable to work in the palette and the spectrum that matches the destination - CMYK for printing, RGB for online display and grayscale for black and white. Changing RGB to CMYK profiles is non (yet) possible on mobile devices.
To display and impress colors
The artist should embed a color profile in the finished artwork that matches i of two destinations: a webpage or a printing company. This is of import because the colour palette for printing is much smaller than the palette of a computer screen. If the artist sends a painting to the printer that has the RGB profile for online display embedded, every color that is non available volition in an automated process be translated to neighboring color that can be printed. The result can be disappointing.
This is peculiarly relevant for painters working on mobile apps because they have the RGB contour embedded in their artworks. A desktop painting program should be used to convert RGB colors to a CMYK profile for printing. Most printing companies supply their own profile, tailored to the machinery, ink and choice of paper. They tin can likewise prescribe one of the CMYK profiles that are available in most computers. Some accept files with the RGB contour and convert them to their own CMYK profile.
Colors in browsers
Only 216 colors are standardized between browsers. The creative person who wishes to avoid online color departure has the selection to use the 'web safe color palette'. However this seriously limits the choice of colors.
In conclusion, three things are needed to run across and to stand for colors reliably:
(ane) The screen should exist calibrated.
(two) The artist should pigment with the color palette that matches the destination. If this is non possible, pigment in RGB and convert to CMYK before sending the work to the printer.
(3) The correct profile should be embedded in the artwork, RGB for digital destination and CMYK for a press company.
Colors of prints at online galleries
Galleries utilise RGB files for online presentation to offer physical prints. The RGB color palette is used equally information technology is or auto-converted to the CMYK palette. Small-scale or large color deviations are inevitable, specially if vivid or 'psychedelic' colors have been used. If accurate colour representation is important, the artist can society a proof from the gallery before offer prints. Blessing of a proof can exist mentioned in the description of the painting.
Texture
Texture
Over the centuries fine art lovers take felt the mitt and mood of the painter in brush strokes and pigment. Many discover that a painting without texture is fine in a volume, merely doesn't experience right on the wall. Though a stylus can be equally sensitive to the pressure of the hand every bit a traditional castor, and the pressure tin exist made visible on the screen, a digital painting is entirely apartment. Some artists accept flatness equally a property of digital painting. Many impress or project their work on a physical carrier and pigment it over, thereby using the estimator every bit a preparatory device and sacrificing the digital characteristics. Brushstroke gel is widely used to simulate castor strokes on a printed sail.
Painterly development
Painterly evolution
A keen multifariousness of digital tools brings the artist new ways to express thoughts and feelings. On the negative side, the more the estimator facilitates their work past offering piece of cake imports, taking over painting processes and offering a wide assortment of styles and transformations, the more difficult it becomes for painters to develop their own idiom, to have distance from images that are already created and to make the voice of the computer secondary to their own.
The pick for an app narrows to some extent the evolution of the artist by limiting him or her to the possibilities and the style of the software. Development is a process of interaction. Apart from making a considered choice, the adventure that a software developer volition not proceed up forwards or astern integration or accept out and sell vital parts of the plan should exist taken into account. In such a case paintings may no longer be available for transfer or printing. Beneath is a famous case. Such dramas can e'er occur, merely the risk is reduced if the software is owned past, and bought from, a company instead of an individual.
Brushes
A notorious case in the young history of digital painting is the enlargement software that was part of the popular Brushes app for raster painting. Brushes recorded all the painter's actions on the iPad, which could and then be replayed on a larger canvas on the desktop. Until 2012, Brushes was the only raster programme that offered enlargement without loss of resolution, a unique characteristic that enabled digital raster painters for the start time in history to testify and sell their work. David Hockney was the kickoff well known painter to surprise the fine art world with very large prints of raster paintings made on the iPad. His exhibition 'A bigger picture' at the London Royal University of Arts between January and April 2012 made Brushes wildly pop.
In September 2012 Brushes' developer Steve Sprang abruptly disabled the enlargement feature. Expressions of protest, anger and despair at Flickr, Github and other forums could non remedy that all paintings were trapped in the Brushes app at the size of a postcard, unfit to impress, exhibit or sell. A whole generation of digital painters and teachers was forced out of Brushes, a silent exodus at a fourth dimension when Hockney's expositions of enlarged Brushes paintings attracted give-and-take wide attending. Soon, Procreate introduced enlargement by recording strokes and actions on a larger canvas . H igh resolution enlargement was again available for raster paintings, but g any painters had lost the labor of several years. They likewise suffered a setback in painterly evolution equally they had to learn how to interact with Procreate or ArtRage, the main alternatives to Brushes and very unlike to use .
Collecting digital art, assessment
Collecting digital fine art, assessment
Calibration
In club to eliminate the color bias of the individual screen, it is important to regularly calibrate (see 'about colors').
Sample
Even with proper scale, it is difficult to assess the look and feel of a painting online. Colors to some extent vary with the physical carrier of the artwork and with the blazon of screen of the spectator. Moreover, many online colors in the online presentation just can not exist printed at all, even with the right color profile embedded. The all-time way to judge a digital painting is past a sample. It should have at least the size of a postcard, be printed on the chosen physical carrier (paper, acrylic glass, aluminum etc.) and executed with the aforementioned resolution and by same printing company that prints the final artwork.
Browsing online galleries
Collecting digital art starts with browsing and research. To browse the many online portfolios is non yet as easy and pleasant every bit it can be. There is a bang-up deal of room for improvement in search algorithms. At the time of writing the search process has several serious limitations.
- Limitations by choice
Galleries with 'follow me' and 'thumbs-up' features rank artists by their number of followers, number of likes, and number of paintings in their portfolio. The creative value thus measured results in increased visibility for some and decreased visibility or invisibility for others in search results. Though stars and thumbs are a mutual mode to valuate all kinds of products, application to art and literature is an issue. Some critics take posited that the acquisition of thumbs-up and likes is not an indication of artistic quality but of social media skills.

- Limitations by lack of information
Despite the invitation at some galleries to filter for mainstream digital media like 'vector', 'raster', 'fractal', 'new photography' etc., as yet few are able to alive up to promise. It should be realized that a collector normally does non know the proper name of the artist. Therefore, if the medium search key doesn't part properly, artists remain invisible. The quality of a search car is easily assessed from the results. If information technology is practiced, a more or less homogenous grab of paintings in a particular medium is brought up. If information technology presents an breathless mix of all kinds of digital and non-digital media, there is a visibility issue. Search results can be supplemented at other galleries and Google Images.
Information virtually the software that is used to create the painting is seldom available. In social club to appreciate originality and technical skill, to distinguish what comes out of the app from what comes out of the artist and peradventure to judge if art claims are justified, some collectors would probably like to know which program was used to create the painting. (Visit Ben Guerette's A Blog appArt for a wild multifariousness of styles and technical skills that are a property of the software.)
Information virtually resolution or the number in a limited edition are too often not yet included in artwork descriptions.
- Other limitations
Search results are oftentimes dominated by big numbers of images by only a few painters. If collectors tire from then much homogeneity and determine to resume at another fourth dimension they volition have to become through the same images once again.
Some galleries lower the resolution of paintings to speed upward browsing, which results in blurred images. While frustrating to artists, information technology deprives collectors of the more time-efficient method of judging precipitous minor-size images at first sight.
Ownership
It remains of import to buy from a trusted party. While most digital painters are still alive, their work can be bought straight at their website or via a link from their homepage to an online gallery.
Buying directly from the artist has pros and cons. The color quality of the print tin be a pro, if the artist will embed a proper CMYK color profile for printing, make corrections when needed and has the work printed at a professional printing company. Many galleries use RGB files for printing, with pocket-sized or larger colour deviations. On the other manus it is non like shooting fish in a barrel for individual artists to friction match the attractive brandish and professional framework with safe payment, delivery and sales conditions that online galleries offer.
If features similar an canonical colour proof, a sample, a manual signature, protection confronting duplication and a certificate are not mentioned in the description of the artwork, the collector tin can ask the artist to make these provisions. For prints that are produced by the gallery, a signature and a barcode or other protective measure can usually be arranged by having the artwork sent through the artist.
-
Gallery of preset styles and conversions
Market for digital art, prints
Market for digital fine art, prints
The marketplace for digital art is gradually maturing. Collectors start to realize that digital painting is a new visual linguistic communication that tin't be expressed with traditional means. Many bug take been solved. Color representation has become fairly reliable thanks to calibration and the employ of color profiles. Digital and physical asset direction and a responsible handling of digital files have brought the risk of duplication of prints down to an adequate level. Slowly but steadily, digital paintings are finding their style to museums, auctions and galleries where they come across a new generation of collectors.
However many highly professional, even pioneering digital painters lack the technical know-how to get their work out of the computer and into the real globe. Almost rely on an online gallery. The larger galleries offer an abundance of originals and express edition quality prints worldwide with good sales conditions. This relieves artists of technical concerns. On the negative side, if printing is left to the gallery and the impress sent directly to the collector, the artist tin no longer evaluate and if necessary adapt the (color) representation. Physical asset direction such as a transmission signature is somewhat more complicated. There is also a prophylactic concern since the computer of the artist is no longer the only location where a high resolution file of the painting is stored.
Quantity quality convention, limited print editions
Quality-quantity convention, limited print editions
In traditional painting, the numbering of a limited edition by convention follows a quality/quantity notation 'i/n' in front of the artwork. Where 'i' indicates a rough ranking of the individual impress according to technical and aesthetic quality and 'n' is the size of the edition. Since all prints of a digital artwork are identical, 'i' has no other meaning than to let a heir-apparent know how many prints are still available. The significant of 'n' is still the aforementioned: the size of a limited edition has economic significance for collectors. As in traditional painting, the size of 'n' is prepare past the artist prior to the first sale. The creative person keeps register of the number of copies that are sold. Open series are referred to as '∞' and numerically unique prints as '1/ane'. In the automated printing procedure, the unnumbered run-up prints that are traditionally labeled every bit 'E.A.' (epreuve artiste) or 'A.P.' (artist's proof), can nevertheless occur.
Certification of a impress
Certification of a print
A certificate is a document that accompanies the print and bears a marker of identity such as the signature of the creative person, often supplemented with some other personalized sign, watermark, bar lawmaking, fingerprint or hologram which matches an identity mark on or in the print. It contains a copyright declaration, distinguishes betwixt an original and an open up or closed edition, states the size of a express edition. Importantly, it informs the buyer of the status of the source file: whether the copyright will be destroyed, reserved for the artist, or transferred to the buyer, if the file is sold. A Certificate of Unicity for a numerically unique print ('original' or '1/1') a Document for a Limited Edition and a Document for an Open Edition is regularly updated and freely available on this site.
Market for digital fine art, digital file equally NFT
Marketplace for digital art, digital file as NFT
NFT
NFT (or 'not fungible token') is a unique code that identifies a digital work and links it to its creator, making it unique. NFT provide buyers with proof of actuality and buying, using advanced encryption. They can be traded online in cryptocurrencies on various platforms. Just like the currency itself, all subsequent transactions are verified in a decentralized fashion by many individual computers in a network. In the process they grade a 'blockchain' which serves every bit a public ledger.
The bright side
An entire generation of digital painters, pioneering a new medium, have experienced for decades that the doors of fine art galleries remained airtight. Their work was nonexistent. Information technology remained largely without resonance, without critical cess and without sales. The principal causes were the physical flatness of a print compared to a traditional painting, a nd the (incorrect) assumption that a digital piece of work can not be unique. After all, a digital artwork is and tin but be, an automated print, and a print could exist multiplied indefinitely. Now the source file is existence sold as unique, not to hang on the wall simply to collect and resell. It'south not new that a digital file tin be uniquely identified with its creator: trusted time-stamping and the expert old ISBN exercise exactly the aforementioned. Simply NFTs come with sophisticated trading paces, new currencies, nice charts, new concepts and a new vocabulary. For the first time a market arises. Moreover, thank you to the secure recording of transactions, artists can earn a royalty on one or more subsequent transactions.
Limitation of uniqueness
I should be noted that the NFT may exist unique, only the source file that is used to generate the NFT remains on the computer of the creator. A digital file can easily exist re-minted by changing a tiny office of it. A different NFT volition then be generated. Even so, once platforms will have implemented authorship verification, roughly similar files will be recognized.
Limitation of royalties
Well-nigh platforms are based on NFTs with the ERC-721 interface. According to Kelly LeValley Hunt, initiator of the Golddust art marketplace, information technology is currently not possible to graft the royalty obligation onto these NFTs. Every bit a effect, the artist receives royalty only as long as collectors are kind enough to stay on the same platform. Most platforms offer NFT transfers to other platforms, royalty obligations are easily annulled. It is expected that royalty contracts volition get platform-contained in the near future.
Property right and Copyright
An NFT is a property right. It does not give the owner the correct to commercial exploitation. Copyright is a dissever right that remains with the creator. However, several platforms make the copyright office of the NFT contract. The buyer then has the right to sell prints and other merchandise . Most buyers don't seem to exist interested in the copyright. They want to collect and show or trade the work. The fact that there may exist many physical and digital copies in apportionment only enhances the status of the possessor. It is often compared to the Mona Lisa: there are countless copies merely to own the one and only painting is something else.
Cryptocurrency, blockchain
The trade in NFT is largely in cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies are not created by central banks simply past users in a computer network, and transactions are not verified past individual banks simply once again past multiple computers in a network. Transactions are timestamped and stored in blocks using cryptography, and the blocks are securely linked together, forming a chain. The 'blockchain' is used as a public ledger.
Energy effect: Proof of Work - Proof of Stake
Ii major protocols are used in this network of distributed computers to create currencies and verify transactions : 'Proof of piece of work' (Pow) and 'Proof of stake' (PoS). Proof of Work, the older of the two, is used by Bitcoin, Ethereum 1.0, and many others. Because of the manner they are designed, they use a huge amount of energy. Last year, Bitcoin alone consumed a staggering 110 Terawatt Hours - over a half percent of global electricity - roughly equivalent to the annual free energy draw of small countries similar Malaysia or Sweden.
The newer 'Proof of Stake' (PoS) protocol allows networks to operate much more energy efficient. Proof of Stake powers Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, Tezos and other, generally newer, cryptocurrencies.
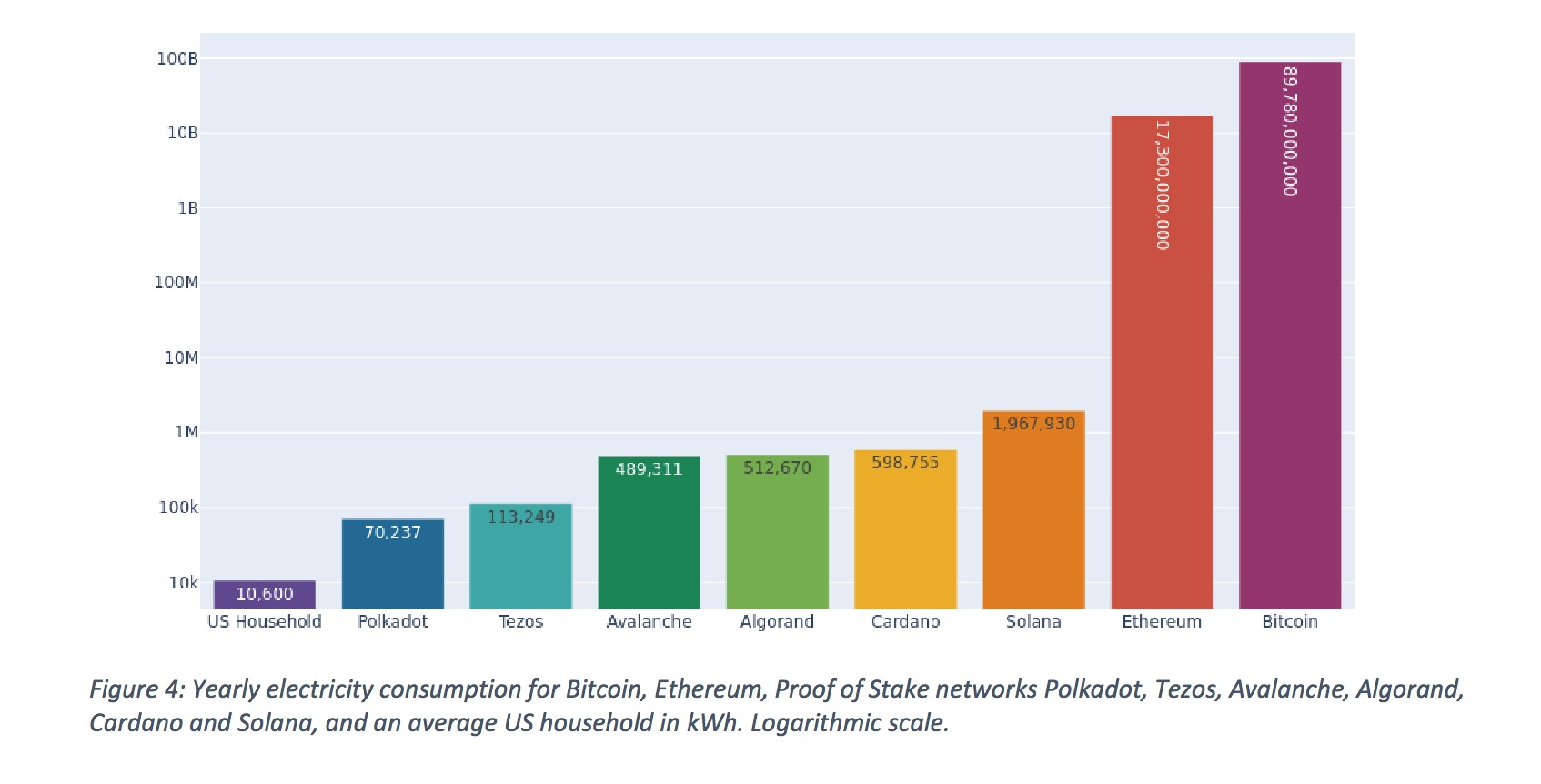
A 2022 study of the Crypto Carbon Ratings Institute compared a handful of PoS-based currencies with PoW-based Bitcoin and Ethereum. Compared to Bitcoin and Ethereum they used less than 0.001% electricity. Note the exponential scale in the nautical chart below : at every adjacent horizontal line , electricity consumption increases tenfold .
Problems with verification
The major problem is that platforms brand petty or no effort to verify who is the artist. Some send an email to the artist's social media account and wait for a reply before they validate the account. The collector is also more often than not anonymous and imitation sales have been used to heave the artist's reputation. Platforms warn collectors to practice some online research to find out if a piece of work is really offered by the artist.
The verification of the artwork itself has the problem that a tiny change in the source file will generate an entirely different NFT. Technically it is piece of cake for a thief to register authorship or for the artist to sell a copy. Automatic computer programs can monitor the platforms for images with a certain corporeality of deviation from the original image, a technique based on 'data altitude' - but so far this tool has not been used.
It would be a big improvement as well as an important contribution to a trusted art market, if sales platforms would make use of existing instruments to verify authorship.
Dark-green NFT art platforms
GREEN NFT Art PLATFORMS
Eco friendly art platforms are (exclusively) based on PoS currencies and PoS transactions. These eat less energy and so for in one case, a 'dark-green' choice is (much) cheaper .
- Hic et Nunc Art, based on Tezos currency and blockchain
- Kalamint,Tezos blockchain
- Screensaver, Polygon blockchain, Matic currency
- Sign fine art, Waves blockchain
A listing of eco-friendly art platforms tin can be found at https://www.github.com/memo/eco-nft.
Many Prisoner of war networks, including ethereum and its ETH, have appear a swith to PoS. This seems to be difficult and will accept some fourth dimension. For the moment, popular platforms like OpenSea, Rarible, SuperRare, Corking, KnownOrigin, Goddust, Makersplace etc. are non suitable for the environmentally conscious creative person.
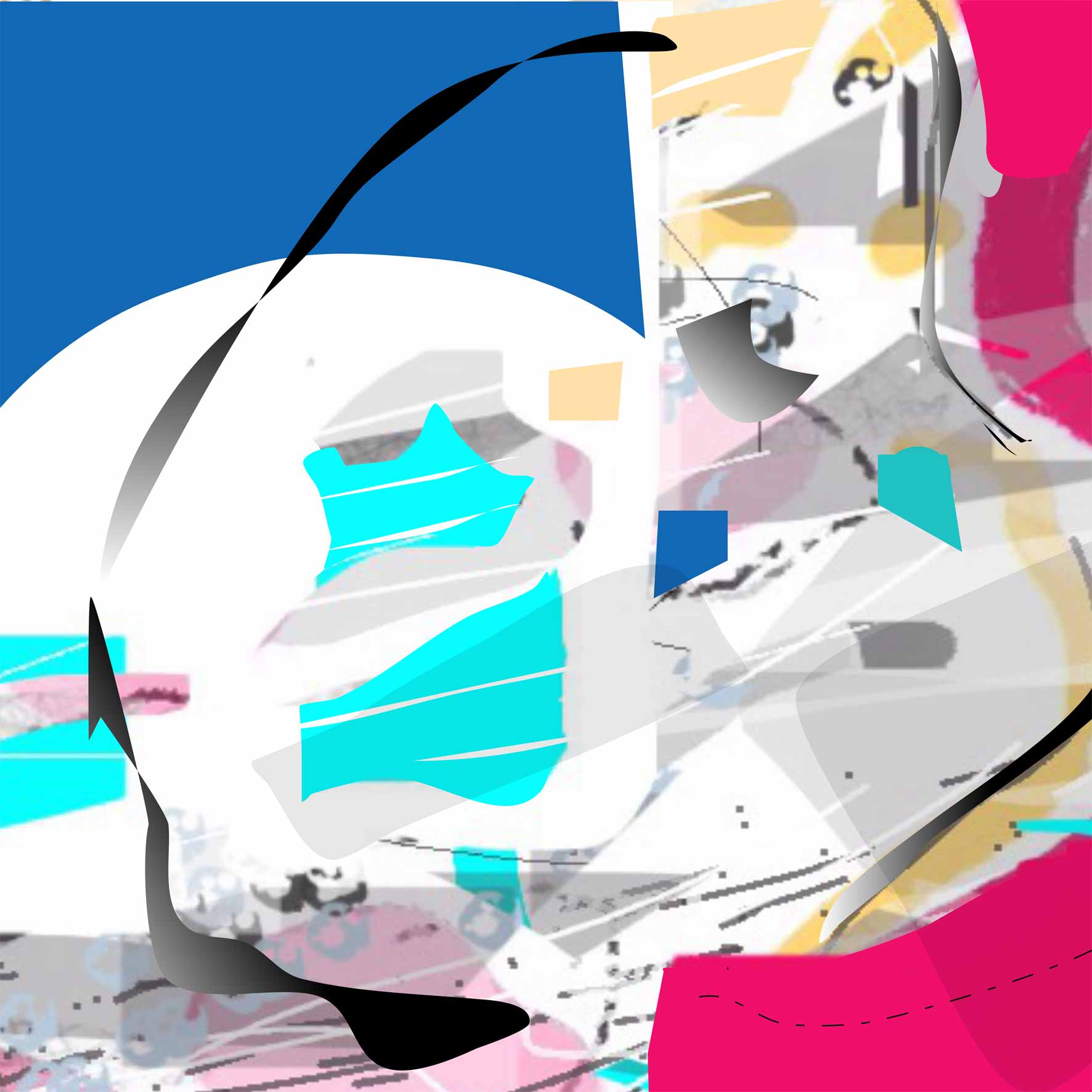

combination of vector and raster
Protecting prints and files, NFT, timestamp
PROTECTING PRINTS AND FILES, NFT, timestamp
It is a mutual misunderstanding that a impress cannot be a numerously unique work of art. It certainly can, and ofttimes is. There are a number of ways to protect uniqueness and limited editions for prints as well every bit digital files.
Precautions
Raster and combined vector-raster paintings tin can exist finer protected past using low resolution and small size files for online display. Stronger measures such as DRM are needed to protect duplication and enlargement of online vector paintings. The artist should protect full-size, loftier resolution files of the artwork by choosing safe methods of transfer and by sharing total scale files simply with printing companies that delete them after employ.
Protection of the print (PAM)
PAM (concrete nugget management) consists of a transmission signature and/or some unique mark that establishes authorship . A GS1 or EAN code tin can be and attached to both certificate and artwork. GS1 codes are issued in over 100 participating countries and tin easily be generated online.
Protection of the file (DAM)
In gild to protect prints it is necessary to protect its digital source code as well. DAM (digital asset direction) can be used to establish authorship of the digital prototype and to prevent it from existence copied and used to produce prints and certificates without marks or with forged marks.
- Digimark
A unique mark can be registered and embedded in the lawmaking of the image. Other than a digital watermark, that is placed over the paradigm and tin can hands exist removed, a digimark survives a diverseness of manipulations and transformations and even duplication by screenshot. Digimarks are optionally supplemented with a search service that crawls the Internet tracing and reporting copies.
- Trusted timestamping
It is possible to securely timestamp a digital certificate, keeping track of its initial creation and subsequent modifications, making it unique. The procedure is based on the same hashcodes that are used to create NFT for artworks. Timestamps rely on a single 'Trusted Authority'. Compared with NFT, trusted timestamping doesn't consume a lot of energy.
- Breezy timestamping
Many online activities and physical representations get out a reliable trace that supports a claim of authorship. Images in ISBN-published books for example, or images published at exhibitions. Images posted in an art customs will ofttimes conduct a timestamp. Images posted on a weblog usually have a timestamp that can be modified by the owner and and then are less useful.
- NFTs
NFT of not-fungible (=non interchangeable) token is a code that is derived from a digital file, uniquely identifying it and linking it to its creator, making it unique. NFTs provide buyers with proof of authenticity and plant ownership for that particular file in a decentralized mode that involves many computers in a network, using avant-garde encryption.
Disadvantages and risks of NFTs
Disadvantages and risks of NFTs
combination of vector and stochastic rules (2022)
ane. Global warming
Artists who offer their art at an NFT platform should realize that 'Proof of work' (PoW) based currencies and transactions are a serious ecology concern. Nature recently calculated that bitcoin alone will be responsible for two degrees global warming in the next 25 years. ETH, the native currency of the Ethereum network, belongs to the same category of giant energy consumers. The Ethereum network can be used with greener currencies that are based on a different protocol, 'Proof of stake' (Pos) simply this does not forbid collectors to fall back on energy consuming currencies within the platform. Fortunately, 'green' platforms, based on 'Proof of Pale' are gaining ground (come across green NFT platforms).
2. Bubbles and crashes
Technical innovation is probably the primary driving factor, but information technology'due south a happy coincidence for NFT platforms that cryptocurrency has been piling up in accounts while there is still little to be bought with it. NFTs tap into large potential need. The way they are presented, with wallets and plenty of charts showing prices rise and fall, plays on the aforementioned appetite for speculation which for many seems to exist the chief allure of cryptocurrencies. Artists and collectors must first purchase cryptocurrency. To a large extent, fine art seems to be bought for the purpose of selling for a quick profit. The new market, so foreign to the nature of art equally representative of permanence , may well turn out to be a double grade of speculation, unique in economic history and perhaps not without macroeconomic risks.
3. Theft of buying
In December 2021, New York's Ross + Kramer Gallery was robbed of NFT valued at a total of $ii.ii million at NFT platform OpenSea. The thief seemed to have sold off many of the pieces. With the help of the buyers, the damage was apparently limited. But it drew attending to the fact that OpenSea apparently did not verify if a seller owns the NFTs.
4. Theft of authorship
A growing number of artists accept online images of their fine art stolen, minted as unique digital assets, and offered for sale on NFT platforms. DeviantArt, an large online community for digital artists began monitoring NFT platforms for theft of their users' work in the fall of 2021. By January 2022 it had sent 90,000 alerts well-nigh possible fraud to thousands of their users. The Guardian quoting DA's chief operations Moti Levi, wrote that automatic calculator programs (bots) had been attacking the site, scraping whole galleries of artists' works. The pieces would afterward appear on NFT marketplaces, often with artists' names and watermarks withal attached.
5.Theft
of copyright
In the market place of prints, the number of illegal copies is likely to increase. Every bit yet in that location is no public registration of copyrights on digital art. Fifty-fifty without copyright the owner of an NFT has the digital source code of the image, which makes exploitation technically simple and economically tempting.
6. Financial risks
Sellers of cryptocurrency and providers of digital wallets are not banks. They are no more subject to centralized supervision of their accounts than a baker or a greengrocer. In most countries, the simply check is for money laundering. There are no general agreements near reserves or compensations if accounts are hacked and plundered. In March 2022, hackers gained access to private keys used to validate transactions on the Ronin platform and stole $625 million in cryptocurrency.
In addition at that place is the risk of strong volatility of the currencies.
How to choose NFT platform
How to Choose NFT platform
NFT platforms are mountains of all believable styles, techniques, directions and formats. Besides art, even the well-nigh exclusively curated platforms offer an incredible amount of domicile industry. The possibilities to filter and search are express and it is extremely difficult for private artists to brand themselves visible. One solution is to build visibility on social media, web log, homepage or art customs, and from there link to the NFT platform.
Since it isn't yet possible to choose platforms for their more or less homogeneous supply of well-defined directions in digital art, while the divergence in ecological footprint between the platforms is huge, it makes all the more sense to allow environmental considerations make the deviation. It besides seems a good selection to expect. There volition be more 'green' platforms, a better verification of authorship, a better understanding and more than homogeneous presentation of art directions . Terminal but not least, royalty contracts will probably become platform independent.
Links
LINKS
Brushstroke gel: Water-soluble acrylic polymer containing a UV inhibitor which helps protect a painting from yellowing and fading. Also used to recreate brushstrokes on digital paintings printed on sail. http://www.artandframingsolutions.com/BrushstrokeGel.htm
Blogs:
Don Archers web log, Digital art, artists and commentaries
Color calibration:
General information
Spyder calibration sensor
Carriers for digital painting:
Xpozer, Prints on polyester coated newspaper, floating, unframed mountain (sRGB contour accustomed)
Whitewall, Prints on Hahnemuele paper, sail, aluminum, dibond, perspex, (printer'south color contour supplied)
Drukwerkdeal, Postcards, large format prints on dibond and brushed aluminum, postcards (printer's color profile supplied)
Certificates:
Certificates For original, limited and open edition
Conversion:
Automatic conversion, photos to paintings, drawings and cartoons
Waterlogue, Automatic conversion of photos to paintings, drawings and cartoons
Enlargement, digital:
Many programs listed
Oneone perfect resize, (enlargement correction)
ZoomPro5, Ben Vista
Enlargement, manual (project of physical and digital prototype on walls, canvas etc.):
Artograph
Beamers (choose a led beamer to work in daylight)
Fractal fine art:
Fractal fine art, video1
Fractal art, video2
Fractalart
Galleries, online:
Absolute Arts
Flickr
Gaac
MOCA
Saatchi online
Galleries, physical:
Agora
K16 Keizersgracht 16, 1015 CP Amsterdam, NL)
Manus painted copies:
Dafen Hamlet, Mainland china:
Marker, barcode, digimark, hologram (impress and digital image protection): Museums: Photo art and artist portfolio: Programs for painting on iPad and iPhone: Programs for painting on PC and Mac: Programs for computer generated painting: Programs for vector painting: Registration: Style: Vector art: Vectorization, online (raster to vector conversion):
Barcode registration GS1
Digimark (invisibly embedded watermark with tracing option, a Photoshop plug-in)
Security hologram
MOCA Museum of Calculator Fine art (MOCA) of New York Country University offers emerging directions in digital art an online platform since 1993. Almanac juried competition in digital art, catalogue.
Flickr
Brushes (raster) (for online brandish merely, enlargement feature for printing no longer available)
Adobe Eazel (raster) (no undo choice)
Adobe ideas (vector) (in combination with Adobe Illustrator)
Paintbook Penultimate
ArtRage (hybrid, with scripting)
Procreate (enlargement for printing, max. canvas depends on device)
Inkpad (vector, some features no longer available, low resolution for PNG and jpg export)
Overview
Adobe Photoshop CS6
Corel cartoon
Fractal Arts
FractalScapes (iPad)
Fractoscope (L-systems, iPad)
ImageSynth (Stochastic rules iPad)
Overwiew of vector programs and file formats
Adobe Illustrator
Adobe ideas (iPad) (in combination with Adobe Illustrator)
Inkscape(open up source, desktop)
Photoshop.com
CorelDraw for Windows
For artwork on paper
A Blog appArt, An overview of styles and features of apps and painting software by Ben Guerette
vector art, video
Pno expo
Blood sweat vector
Vectormagic
Autotracer
2013-2022 DigitalPainting.be Amsterdam - Gent
Source: https://www.digitalpainting.be/
0 Response to "How to Turn a Drawing Into Digital Art With Corel Painter 2015"
Post a Comment